Electronic instruments: From birth to the future
Electronic Musical Instruments are born in simulation
At the end of the 19th century, the famous instrument at the beginning of the birth of electronic instruments, the Telharmonium(①), is an electronic organ with a large area - the first electronic instrument to adopt the principle of algorithmic synthesis and additive synthesis, which can imitate the sound of the flute, the oboe, the trumpet, the horn and the cello.

Telharmonium:By User Chris 73 on en.wikipedia - [1], Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1347777
Invented in the early 20th century, the Ondes Martenot has appeared many times in the works of the composer Messiaen, and the original model sounds like a flute/ocarina; Later models sound like clarinet high register, bassoon low register, some like strings.
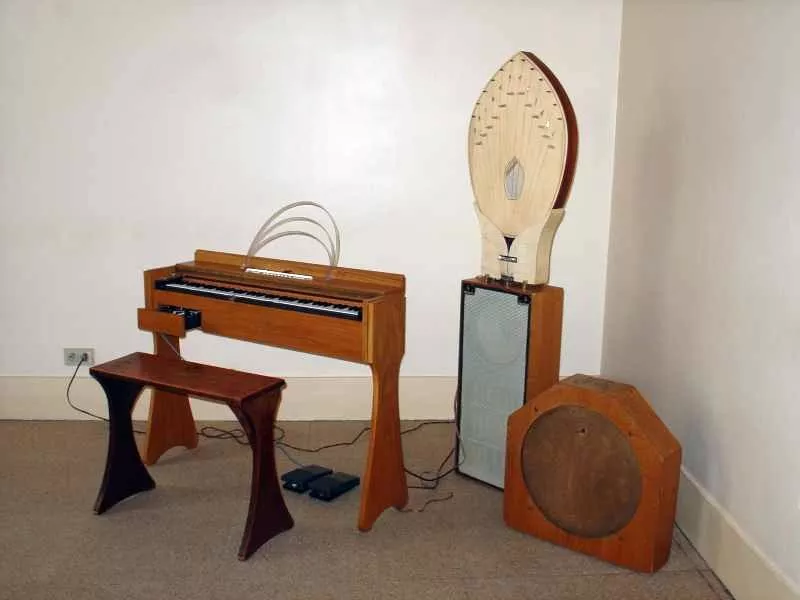

Ondes Martenot Image Credit: By ja: User: 30rKs56MaE-ja: Portraits: Ondes_martenot. JPG, CC BY sas 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=1019724
Some electronic instruments copy the acoustic instruments in the way of playing, and simulate the sound directly, some instruments have innovative breakthroughs in the way of playing, and the sound is still simulated, such as the famous Taylor’s sound (Theremin) (③), which is played in the hands of the performer, emits a violin-like sound.
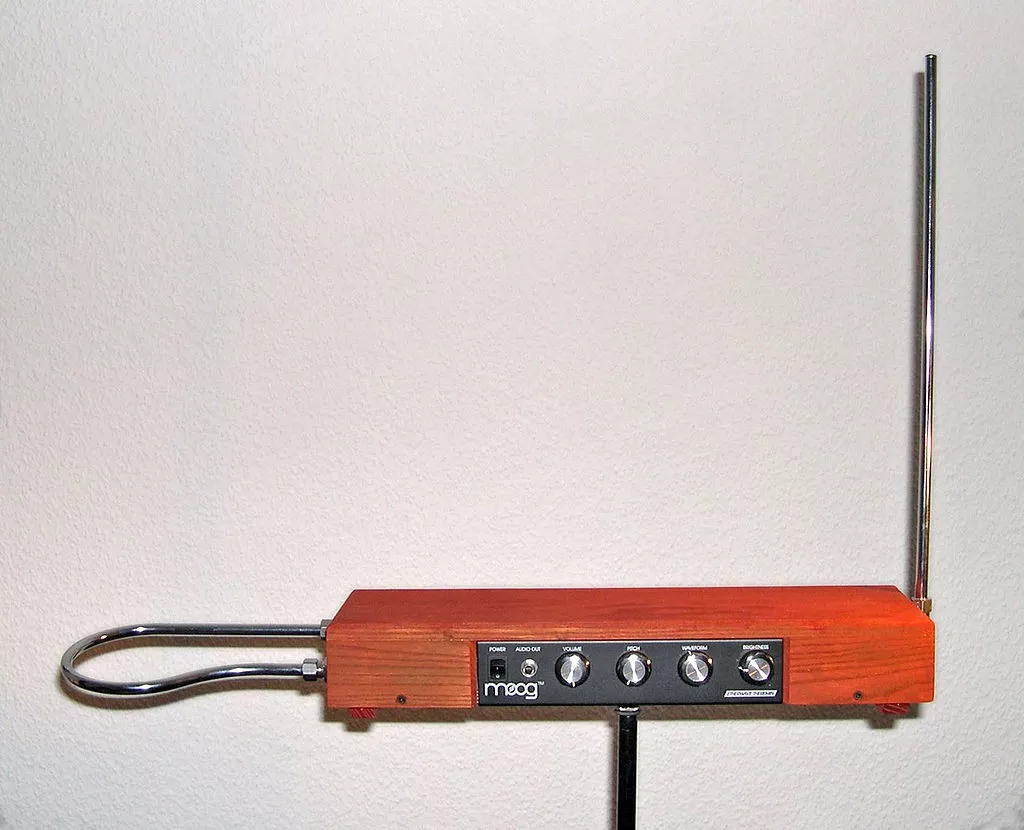
Theremin image: By Hutschi - Self - photographed, CC By sas 3.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=422180
Since the purpose is simulation, if the acoustic instrument sound can be directly controlled as the material, that is, the sound is generated through the so-called sample synthesis principle, the effect should be the most direct. However, due to technology, cost and other reasons, the early commercial electronic Musical Instruments did not adopt sample synthesis, but are in the vacuum tube analog circuit, using the algorithm synthesis principle to produce sound. In this way, from the sound principle to the shape and the acoustic instrument are completely different, so the simulation is not in place, only some like, or even only a little like the shadow. However, fortunately, the simulation can not be in place, in my opinion, it is not in place, forcing the early electronic instruments have to give up the pursuit of resemblance and the pursuit of spirit, have to use the “freehand” method to imitate, but the early electronic instruments have a certain characteristics of the timbre. This feature can be said to be a by-product of simulation, or it can be said to be the result of unintentional insertion of electronic instruments in simulation during the ignorant period.
In the late 1950s, the birth of computers brought digital electronic Musical Instruments, referred to as digital Musical Instruments or digital Musical Instruments, are electronic Musical Instruments that can be synthesized by algorithms and can also be synthesized by sample synthesis principle. But at that time, these software electronic instruments, which were made by vacuum tube digital circuit computers, only stayed in the laboratory, such as the Music N(④) series of computer music languages. The instruments of the vacuum tube era are often both commercial and experimental, so there is no need to describe the hardware electronic instruments in the experimental field of this period. instr1 ; Initial variable iamp=ampdb(p4) ; Convert exponential decibels to linear amplitudes iscale=iamp*.333 ; Amplitude scaling inote=cpspch(p5) ; Convert pitch to frequency klinelineniscale,p6,p3,p7 asin1 oscilkline,inote,1 asin2 oscilkline,inote*.996,1; Slightly lower frequency asin3 oscilkline,inote*1.004,1; Slightly higher frequency asin1=asin1+asin2+asin3 out asin1 endin A Csound instrument program developed from MUSIC N
At the beginning of the birth of electronic instruments, almost all forms of electronic instruments, such as analog and digital; Commercial or experimental; Both hardware and software have appeared. Electronic instruments are also in an ignorant period where the development direction seems unclear - the simulation is not in place, and their own characteristics have not entered the public vision.
Electronic Musical Instruments self-plastic in simulation
The invention of the transistor greatly reduced the size of electronic components, and electronic devices of the same size could perform more complex tasks, such as recording. Sample synthetic electronic instruments can finally surface, from conception to reality. Mellotron (5) is the first keyboard instrument that I know of that uses the principle of sample synthesis, which is dedicated to simulating the sound of string bands, and the sound samples are recorded on tape in an Analogue manner.
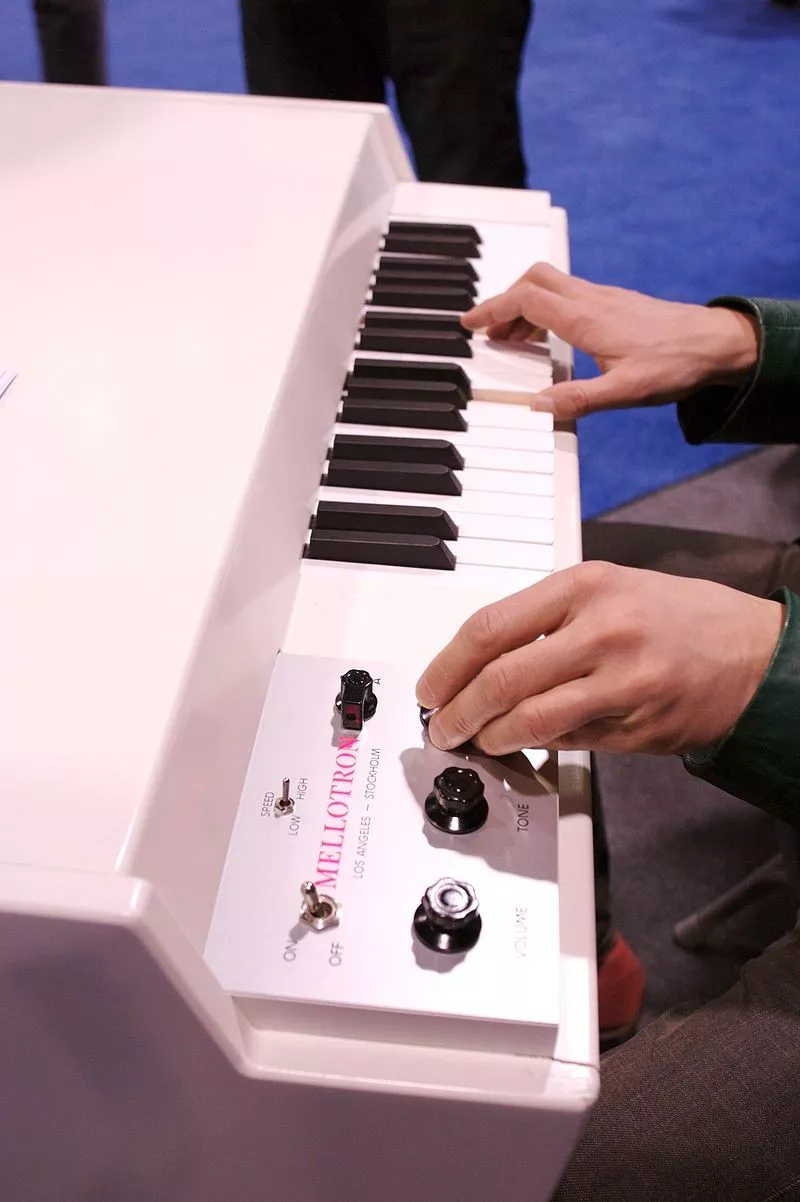

Mellotron Image Credit: By Buzz Andersen from San Francisco, California, United States - Mellotron | NAMM 2007, CC BY-SA 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=2801145
Although sample synthetic electronic instruments finally appeared, the commercial simulation army of the transistor era consisted mainly of algorithmic synthetic electronic instruments. The success of the Moog synthesizer (⑥) in the 1960s and the Jupiter synthesizer (7) in the 1970s marked the maturity of the commercial analog electronic instrument (synthesizer) technology in the form of algorithmic synthesis of timbres.
Moog Synthesisers image: By Chad - Moog., CC By sas 2.0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=9607366
Image: Roland Jupiter - 4 By Automaton399 - Own work, CC0, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=23093620
Although the traces of simulation are still very obvious, such as the now familiar electric piano (E.Piano), synthetic strings (Synth String), synthetic Drum (Synth drum) and other timbre are products of that period, but these sounds have the characteristics of electronic Musical Instruments “freehand” simulation, and on the basis of simulation, Some fresh sounds are produced, such as the bottom tone (Pad). What is more interesting is that from these synthesizers, sounds that have never been heard in nature, such as spaceship sound, synthetic Lead sound (Synth Lead), etc., the characteristics of electronic musical instrument sound are gradually revealed, and the identity of sound protagonists in science fiction films has become well-known, and the self of electronic Musical Instruments seems to “wake up” from the ignorance. The goal of simulation is to become others, but let the electronic musical instrument’s self gradually grow, it can be said that electronic Musical Instruments have been self-shaped in simulation. In terms of digital instruments, hardware commercial digital instruments have not yet appeared on the stage of history. The Music N series of software electronic instruments continues its journey of experimentation full of possibilities in the transistor age.
In the transistor period, although the sample synthesis finally appeared, the simulation force is still strong, but it makes the commercial analog electronic instruments self-plastic sound characteristics, coupled with the unique characteristics of the experimental field of software electronic instruments, self-plastic forces seem to have the upper hand.
Transistors were quickly replaced by integrated circuits, large-scale integrated circuits, and very large scale integrated circuits. The popularity of integrated circuits has taken some computer music technologies out of the laboratory and made it possible to use them for commercial digital Musical Instruments (computers that specialize in synthesizing sound). In the early 1980s, frequency modulation (FM), as one of the algorithm synthesis technologies, achieved the popularity of the digital synthesizer DX7(⑧).
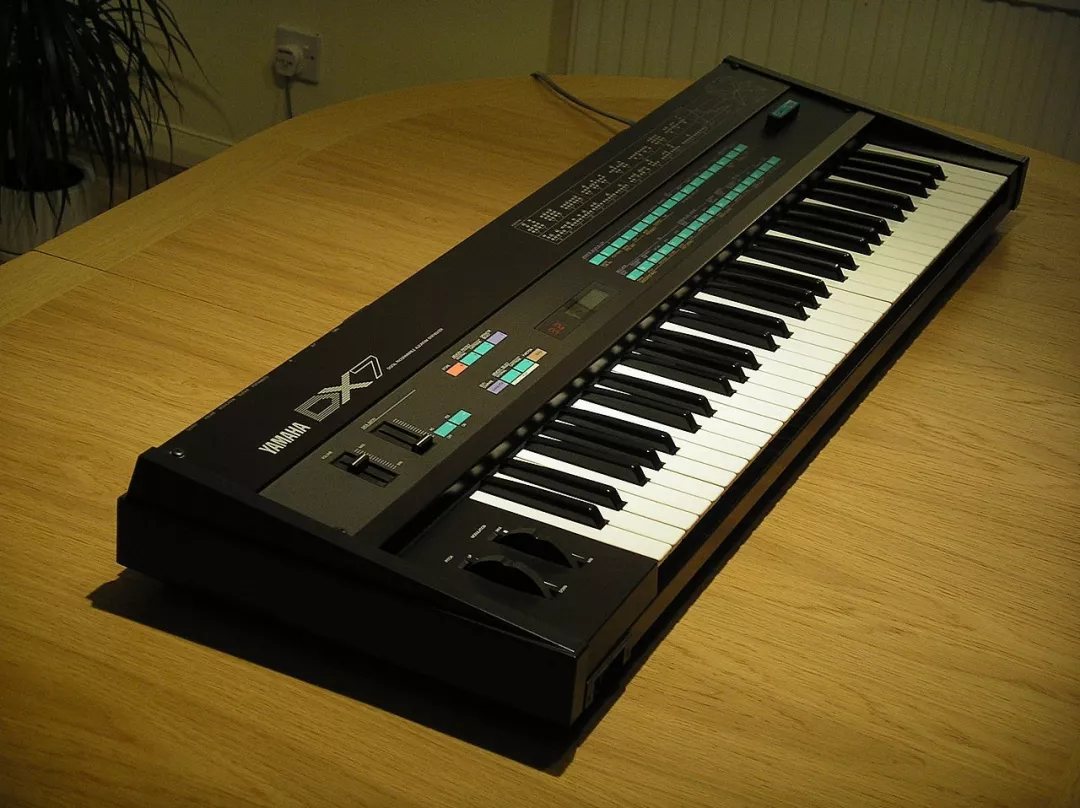

DX7 image: By iixorbiusii - Steve Sims, Public Domain, https://commons.wikimedia.org/w/index.php?curid=12379187
At this time, commercial digital instruments replaced the discontinued commercial analog instruments, leading the way of self-plastic commercial electronic instruments, although the simulation class still accounts for a large proportion of timbre, but the timbre with its own characteristics also emerged in large numbers.
In the mid-1980s, Csound(⑨), derived from the MUSIC N series MUSIC 11, became a darling of the experimental world. Transistor/Integrated circuit In the early days, there were some hardware electronic instruments in the experimental field, such as the Radio-baton (baton), which was born in the laboratory to solve human-computer interaction problems.
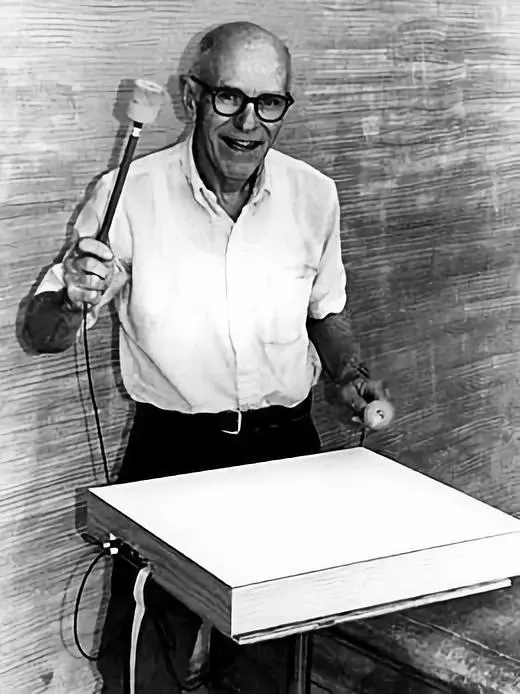

Max Mathews, the father of computer music, plays Radio-Baton. Image credit: By Finnianhughes101-Own work, Public Domain
In the early days of transistors/integrated circuits, commercial electronic instruments that have always “done it” and experimental electronic instruments that have always “done it themselves” have for the first time jointly complied with the fate of self-plastic, and this stage is called the self-plastic stage of electronic instruments.
Electronic instruments are upgraded in simulation
Soon, in the late 1980s, the application of Digital Sampling technology triggered a wave of cloning simulation.

[Photo] M1 Image Credit: BY Warren B. - originally posted to Flickr as IMG_1940.JPG, CC BY-SA 2.0
Synthesizers that use sample synthesis technology, particularly the M1, stop the development of commercial digital instruments and start to follow the simulation in all areas, and even a specialized electronic instrument, the sampler, has emerged. The AKAI S1000(⑫) sampler was one of the most popular hardware samplers of the time.
.webp)
AKAI S1000 Image Credit: JPG BY Akai-S1000.JPG: DG3YEVderived work: Clusternote (talk) - This file was derived from Akai-S1000.JPG:, CC by-SA 4.0
Sample synthesis technology continues to upgrade, until the 1990s, using the physical model of the VL(ErD) series, represented by the digital synthesizer hardware electronic instruments, reached the peak of the simulation of acoustic instruments sound - from freehand imitation, to realistic cloning, and commercial electronic instruments self-plastic sound has become very small, almost inaudible.
VL1 Image Credit: YAMAHA Virtual Acoustic Synthesizer VL1 Owner’s Manual 1
In the 1990s, MAX/MSP(14), an experimental field which is not in the public eye, was born unexpectedly and is a pioneer of graphic music programming language. However, MAX/MSP is paid software, and the original author developed a free graphic programming computer music language Pure Data(⑮), continuing the road of electronic Musical Instruments.
Graphic programming Computer Music Language MAX program screenshot (adapted from MAX tutorial)
During this period, experimental hardware electronic instruments began to develop into multimedia, such as video capture devices for controlling sound. These hardware electronic instruments have two characteristics, characteristic one, generally rely on a computer music language, such as MAX/MSP; Second, they are generally unintegrated and temporary systems, most of which cannot be reused. Because of the above characteristics, the experimental field of hardware electronic instruments, either belong to a research institution, or belong to the individual artist, did not enter the public vision. Although there are independent, stable, software and hardware combined computer music programming systems such as Kyma(⑯ Persons), they have only been used in a small range due to the high requirements on the user’s knowledge reserve.
Kyma 7 system Image Source: http://kyma.symbolicsound.com/
Dramatically, commercial electronic instruments have been interrupted by their own characteristics, at the turn of the millennium, self-shaping forces in the Digital Analogue Synthesizer, that is, in the digital integrated circuit, using the analog synthesizer algorithm of the transistor age in the form of synthetic sound. “Kill” back, the Nordic module (Nord Modular) is the leader at the time. However, the digital analog synthesizers, which were not popular, were soon discontinued and their traces were difficult to find.
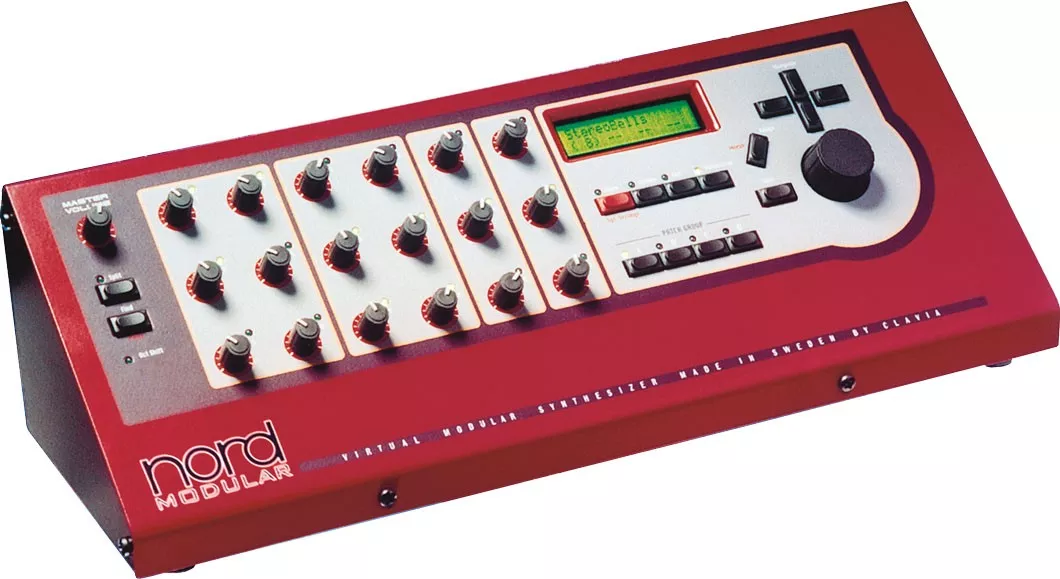

Nord Modular Image Credit: http://www.nordkeyboards.com/
Electronic instruments in the era after the plastic period, simulation forces flocked to, it seems to occupy all commercial electronic instruments at once, did not expect the plastic forces a plan to “kill” out of a short equal, but ultimately failed to hold the situation, electronic instruments fully into the simulation period.
Electronic instruments are differentiated in simulation
In the 1990s, when commercial hardware electronic instruments were in full swing, commercial software electronic instruments quietly stepped onto the historical stage.
Earlier appeared, is the commercial software electronic instrument Reaktor predecessor - Generator(18). Reaktor, as an early representative of commercial software electronic instruments, has been active until now.
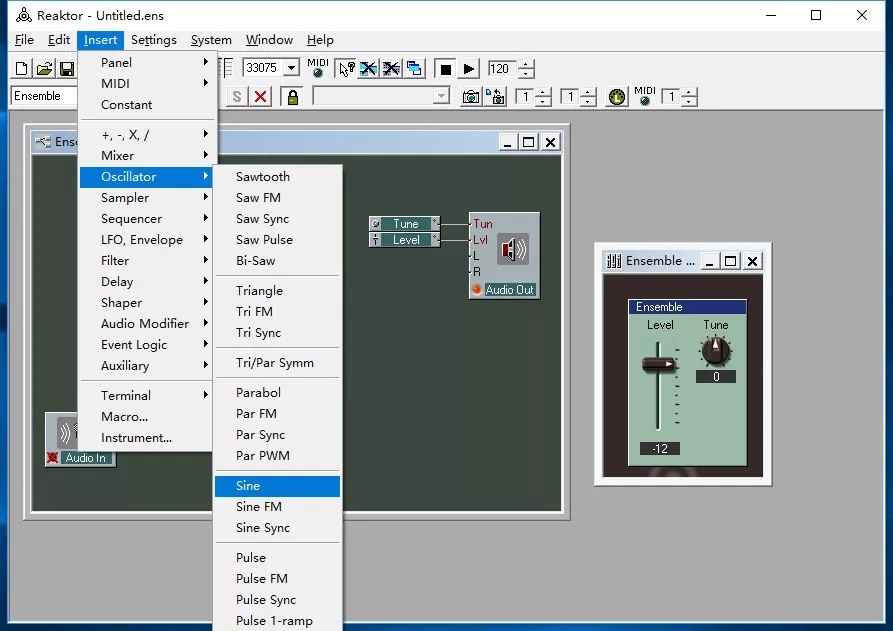
Screenshot of the running interface of Reaktor 2
Soon, almost at the same time as the “retro” digital analog hardware instruments, the Giga Sampler(⑲), a commercial sample synthesizer software electronic instrument, appeared on the stage of history. As the pioneer of electronic Musical Instruments for commercial software of sample synthesis, Giga changed people’s concept and way of working, but for various reasons, it was gradually replaced by its successors.
A screenshot of the Giga Sampler’s updated version, Giga Studio 3, and its instrument editor
After Giga, soft samplers flourished, including the KONTAKT(⑳), which debuted in the early 2000s and is still a major instrument today. Since then, although there have been some algorithmic synthesis of commercial software electronic instruments, the number and scope of use are far less than sample synthesis.
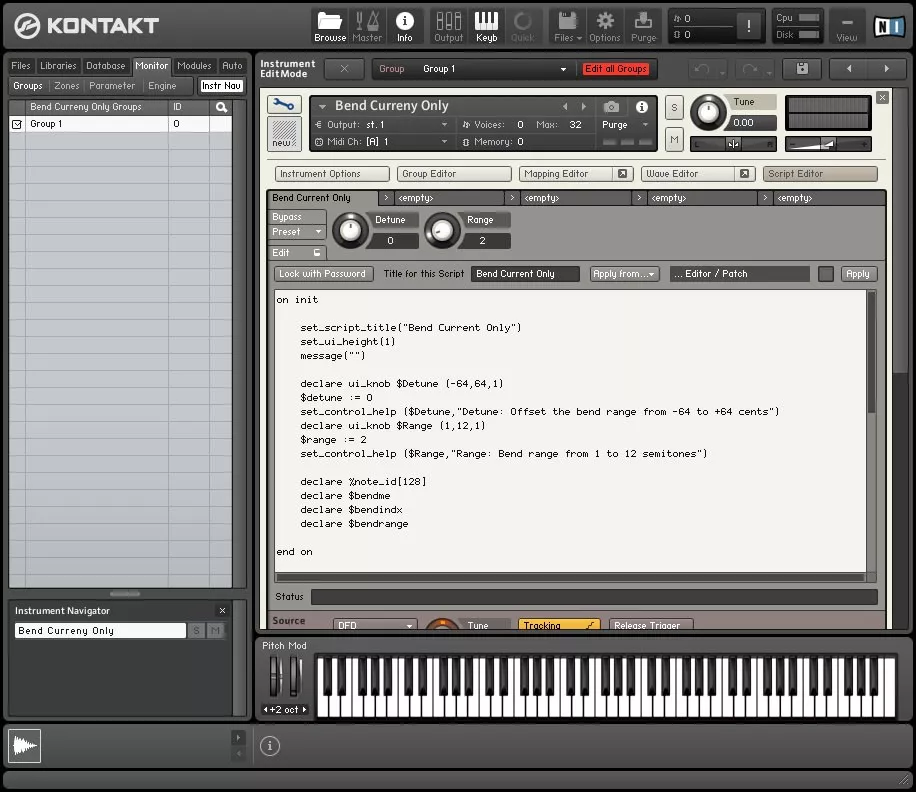
Screenshot of KONTAKT 5 operation screen
The development of commercial software electronic instruments has brought a great impact on commercial hardware electronic instruments. The first is the total demise of hardware samplers; Secondly, there has been a significant decrease in the number of commercial hardware electronic instruments for sample synthesis. There are two trends in commercial hardware electronic Musical Instruments. Commercial hardware electronic Musical Instruments simply do not include sound sources, do not synthesize sound, become similar to keyboard controller, MIDI controller, MIDI mixer, Motion controller and other pure switch shape control equipment, such as the motion controller (㉑) (Leap Motion), which has been widely used in recent years.
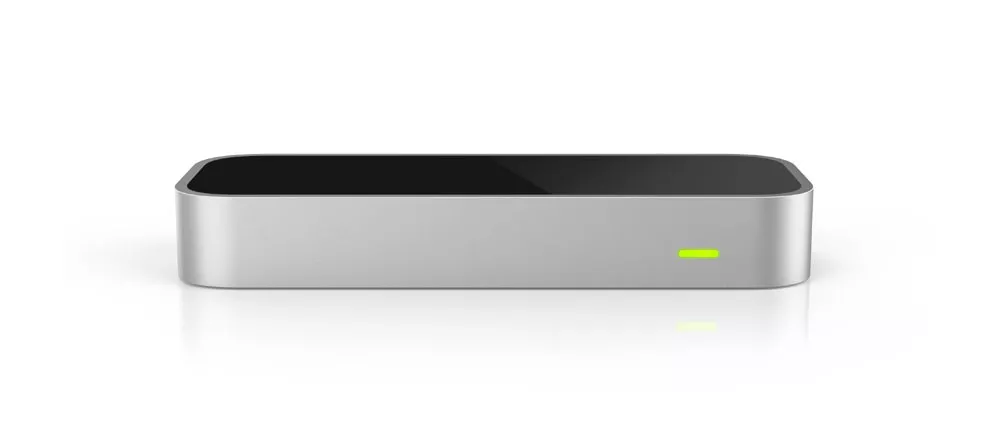

Leap Motion Image Credit: https://www.leapmotion.com/
Algorithm synthesis is another development trend after commercial hardware electronic instruments are generally replaced by soft sound sources (commercial software electronic instruments). In recent years, many commercial hardware electronic instrument manufacturers have begun to produce algorithmic synthesizers. For example, the dedicated retro ROLAND Boutique collection (㉒) recreates many of its historically successful Analogue synthesizer sounds.
Roland Boutique Image Credit: http://www.roland.com/
In addition to Csound, MAX/MSP and many software electronic instruments that continue to explore new sounds in the experimental field, new medium-based experimental hardware electronic instruments begin to appear. For example, by using the open source platform (㉓) (Arduino) and temperature, humidity, light and motion sensors, humidifiers, hair dryers, flash lights and brush strokes can become electronic instruments.
Arduino image Source: https://www.arduino.cc/
These functional instruments that accomplish specific tasks are mostly as dependent and temporary as previous experimental hardware electronic instruments. However, almost all the hardware electronic instruments in the experimental field, including the independent and stable platform hardware Kyma, have not really entered the public field of vision.
Since the 21st century, the commercial electronic musical instrument, which was originally all hardware, has become a large area of software; In the experimental field, software electronic instruments are increasingly combined with hardware. In the general trend of commercial hardware electronic instruments being replaced by commercial software electronic instruments, their respective functions seem to be differentiated. Commercial software seems to have all the sample synthesis, and many commercial hardware has to give up sample synthesis and return to the self-plastic road of algorithm synthesis. In the commercial field, simulation dominates, but in the experimental field, the pace of self-exploration of electronic instruments has not stopped.
Electronic instruments have unconsciously developed some characteristics from the ignorant state of mere simulation. Then in the Analogue circuit period and the early digital circuit, the “self” is more formed; In the later period of digital circuit, under the “blessing” of digital sampling technology, electronic instruments with cloning ability have a great potential to replace acoustic instruments. Nowadays, electronic Musical Instruments are used commercially and experimentally again. Hardware and software; Sample synthesis, algorithm synthesis each leading situation. Hold up the situation, electronic Musical Instruments have fully entered the simulation period.
Electronic instruments # Music history # Music technology # Music future # Music innovation # music development #AI music #Songdio AI
Electronic music experience creation: https://songdio.app/